PCI in a Patient with Triple Vessel Disease (TVD)
Patient Details
Name: ABC
Age/Sex: 59 Years / Male
K/C/O : Hypertension (on Tab Concor 5 mg OD)
Date of Admission: 14-07-2025
Presenting Complaints:
- Left-sided chest pain radiating to shoulder
- Dyspnoea on exertion
- Easy fatigability
- Generalized weakness
Duration: 12–15 days
Initial Clinical Assessment
- Vitals
- BP: 150/90 mmHg
- HR: 84 bpm
- RR: 18/min
- SpO₂: 97% on RA
- Temp: 97.7°F
- Pain Score: 6/10
General and Systemic Examination: Normal findings; no pedal edema, JVD, or murmurs.
Investigations
Hematology and Biochemistry
| Test | Value | Interpretation |
| Haemoglobin | 12.7 g/dL | Normal |
| WBC | 8380/µL | Normal |
| Platelets | 229,000/µL | Normal |
| RBS | 106 mg/dL | Normoglycemia |
| Creatinine | 0.97 mg/dL | Normal renal function |
| HBsAg, HCV, HIV | Negative | No infections |
2D Echocardiography (14-07-2025)
- EF: 50% – mildly reduced
- RWMA: Apical cap and apical anteroseptum mildly hypokinetic
- LVH: Mild concentric
- LV Diastolic Dysfunction: Grade I (E/e’ = 11.1)
- PASP: 10–15 mmHg (Normal)
- Valves: Trivial TR, no AR/MR
- IVC: Normal, >50% collapse
Conclusion:
- Mild LV systolic dysfunction with segmental wall motion abnormality suggestive of ischemia (especially LAD territory)
Pre-procedure ECG
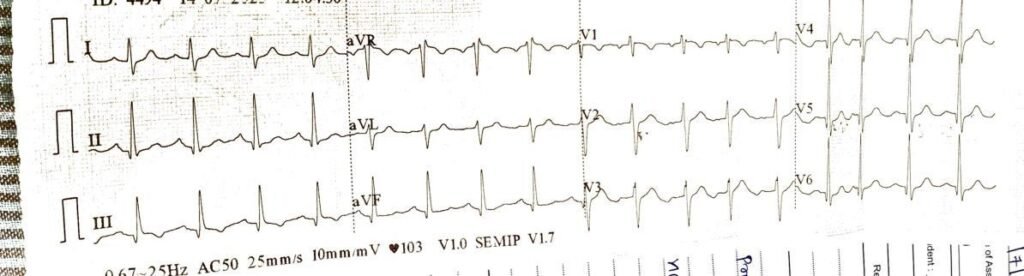
Rhythm:
- Sinus tachycardia (HR ~103 bpm)
Findings:
- T wave inversion in V4–V6, I, aVL
- Poor R wave progression V1–V3
- Incomplete RBBB
Interpretation:
- Suggestive of ischemia in anterior and lateral wallEmergency Decision-Making
Based on:
- Persistent symptoms despite medication
- ECG + echo evidence of ischemia
- Suspected high-risk CAD
Patient shifted for emergency coronary angiography (CAG) via right radial artery.
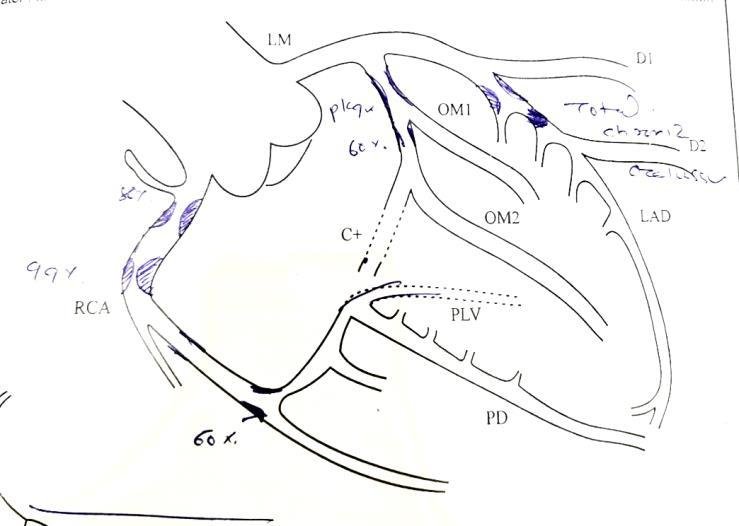
Coronary Angiography Findings (CAG)
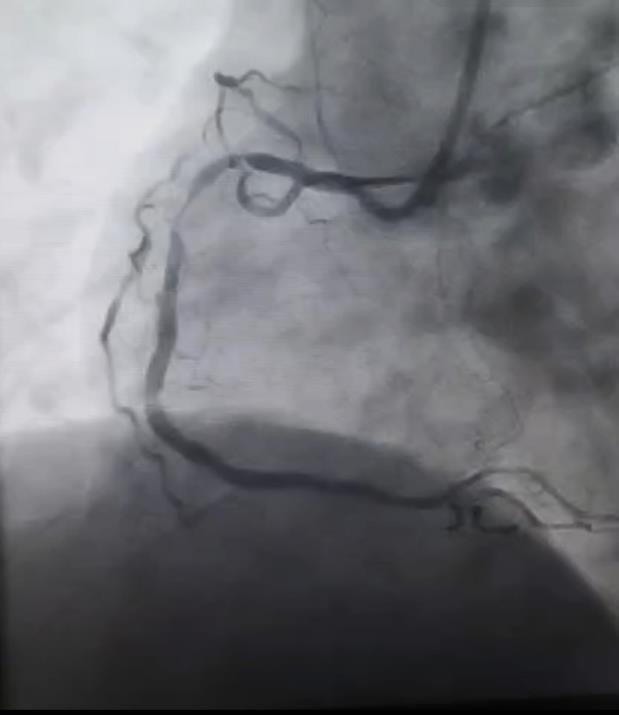
Vessel Lesion
- RCA 99% proximal stenosis, 80% mid stenosis (culprit)
- LAD Total chronic occlusion (non-culprit)
- OM1 60% plaque (non-culprit)
Diagnosis: Triple Vessel Disease (TVD)
Hemodynamics during procedure: Bradycardia, hypotension, hypoxia
PCI Procedure Details
- Indication: RCA was culprit (high-grade obstruction, unstable angina, ECG changes)
Procedure:
- Two Drug Eluting Stents (DES) deployed to RCA
- Access via right radial artery
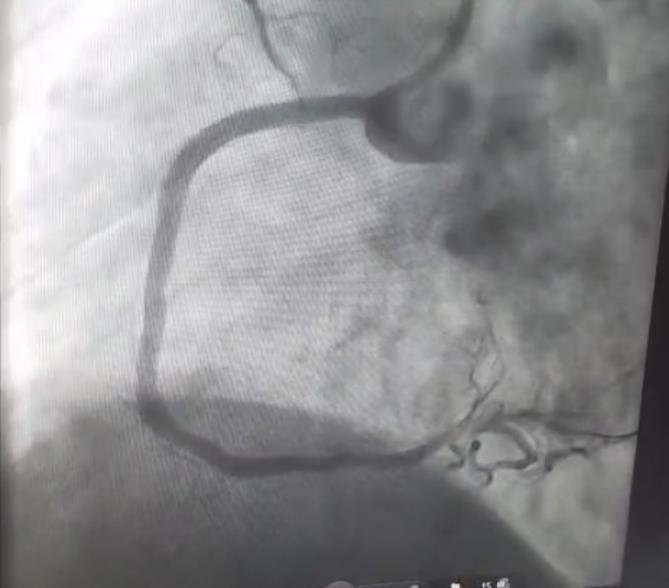
Intra-Procedural Complications:
| Complication | Likely Cause | Immediate Management |
| Bradycardia | AV nodal ischemia (RCA territory) | Inj. Atropine 2A IV |
| Hypotension | Vagal response / Ischemia | Norad infusion @ 2 mL/hr |
| Hypoxia | Transient perfusion deficit | Nasal oxygen |
Mechanism of Atropine:
- Anticholinergic: Blocks vagal stimulation to heart
- Increases SA/AV nodal activity
Mechanism of Noradrenaline:
- α1-agonist: Peripheral vasoconstriction → ↑BP
- Mild β1-effect: ↑ myocardial contractility
Post-Procedure ICU Management
- Patient shifted with radial sheath in situ
- Vitals stable post 2 hours
- No further inotropic/O2 requirement
- Sheath removed uneventfully
- ECG
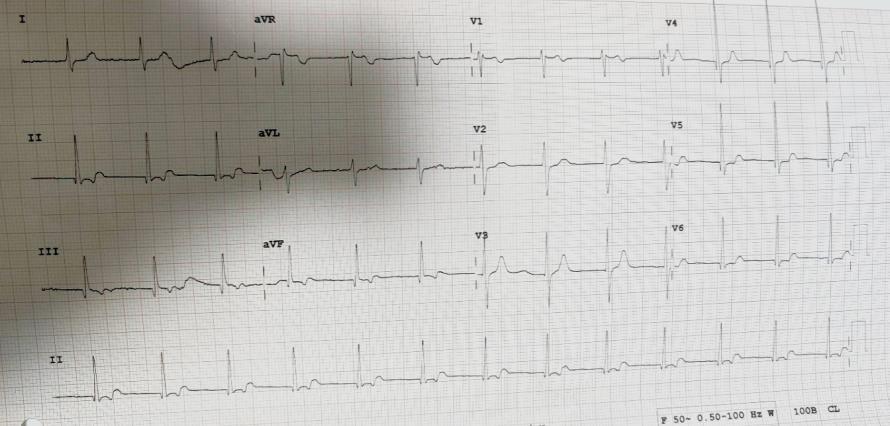
Post-PCI Medications with Justification
| Drug | Dose | Mechanism | Purpose |
| Inj.Nikoran | 48 mg @ 2 mL/hr | Nitrate donor & K+ channel opener | ↓ Coronary spasm, ↑ perfusion |
| Inj.Agramed | 70 mL @ 7 mL/hr | GPIIb/IIIa inhibitor | Prevent acute instent thrombosis |
| Inj.Monocef | 1g IV BD | 3rd-gen cephalosporin | Prophylaxis (ICU setting) |
| Inj.Pantoprazole | 40 mg IV BD | PPI | Stress ulcer prophylaxis |
| Inj.Emset | 4 mg IV BD | 5HT3 antagonist | Antiemetic |
| Inj.NS | 50ml/hr | Hydration | Maintain perfusion & renal flow |
| Tab Ecosprin | 75 mg OD | COX-1 inhibition | Antiplatelet |
| Tab Brilinta | 90 mg BD | P2Y12 inhibitor | DAPT maintenance |
| Tab Rosuvas | 20 mg HS | HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor | Stabilize plaque, ↓LDL |
Clinical Reasoning
- Why RCA was the culprit: ECG changes + echo + anginal symptoms + RCA supplies AV
node - Why PCI was needed: Unstable symptoms + critical stenosis + risk of infarction
- Why no immediate CABG: LAD CTO + RCA culprit; staged revascularization strategy
often preferred in elderly with high-risk lesions
Final Diagnosis
- Triple Vessel Disease (TVD) with culprit RCA lesion, causing ischemic bradycardia
and hypotension. Successfully treated by PCI with DES.
Teaching Mnemonic – “RCA = RAVEN”
- R – Reflex Bradycardia
- A – AV Node Ischemia
- V – Vasovagal Reflex
- E – Ectopy
- N – Nodal Supply Compromised
Suggested Discharge Plan
- Continue DAPT for 12 months
- Lifestyle changes + BP & cholesterol control
- Stress/rest perfusion scan after recovery
- Consider CABG if LAD revascularization indicated
Conclusion
- This case illustrates the importance of rapid recognition and intervention in RCArelated ischemia, especially when conduction abnormalities and hemodynamic
compromise occur. Timely PCI salvaged the myocardium and conduction system,
restoring perfusion and preventing major infarction.
Fun Fact
- In 85% of individuals, the RCA supplies the AV node. Hence, RCA occlusion
commonly causes bradycardia and heart blocks.