The Fire Within: A Battle Against Pancreatic Storm — When Pancreatitis Turns Multiorgan
01) Diagnosis
- Primary Diagnosis: Severe Acute Pancreatitis
- Complicating Conditions: Septic Shock, Acute Kidney Injury (AKI), Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
02) History of Present Illness (HPI)
- Chief Complaints:
- Severe epigastric pain radiating to the back for 2 days
- Recurrent vomiting and abdominal distension
- Shortness of breath, oliguria, and fever for 1 day
- Progression: Pain worsened over 48 hours; patient became drowsy and hypotensive on arrival.
- Associated Symptoms: Fever, nausea, vomiting, breathlessness, and decreased urine output
- Negative History: No history of trauma, gallstones, alcohol binge, or drug overdose
03) Past Medical History
- Hypertension (HTN) – on Amlodipine 5 mg OD
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) – on Metformin 500 mg BD
- No past ICU admissions or surgeries
- No known allergies
- Relevance: Both HTN and DM increase risk for multiorgan dysfunction and worsen prognosis in sepsis.
04) Physical Examination
- General:
- Toxic appearance, anxious, in distress
- Pallor +, Icterus +, Pedal edema mild, Cyanosis + (peripheral)
- Systemic Examination:
- CVS :- Tachycardia, no murmur, normal S1S2
- RS :- Bilateral coarse crepitations (suggestive of early ARDS)
- CNS :- Drowsy but arousable (GCS 10/15)
- Abdomen :- Diffuse tenderness, guarding, sluggish bowel sounds
05) Vitals on Admission
- HR: 126 bpm
- BP: 78/48 mm Hg
- RR: 32/min
- Temp: 101.8 °F
- SpO₂: 88 % on 10 L O₂
- GCS: E2 V3 M5 = 10/15
06) Echocardiography (ECHO)
- LV size: Normal, EF 60 %
- No RWMA
- No valvular pathology
- No pericardial effusion
07) Investigations (Baseline – Day 0)
| Test | Result | Interpretation |
| CBC | Hb 10.8 g/dL, WBC 21,800/mm³, Plt 160k | Infection |
| RFT | Urea 86 mg/dL, Cr 3.1 mg/dL | AKI |
| Na⁺ | 132 mEq/L | Mild hyponatremia |
| K⁺ | 4.9 mEq/L | Normal |
| Ca²⁺ | 7.5 mg/dL | Hypocalcemia (poor prognostic sign) |
| LFT | AST/ALT 88/91 IU, TB 2.3 mg/dL | Hepatic stress |
| ABG | pH 7.28, pCO₂ 28, HCO₃ 16 | Metabolic acidosis |
| Lactate | 4.8 mmol/L | Severe sepsis |
| Amylase/Lipase | 600 U/L / 1200 U/L | Diagnostic for pancreatitis |
| PCT | 9.1 ng/mL | Severe bacterial sepsis |
| CRP | 210 mg/L | Inflammatory marker |
| INR | 1.4 | Mild coagulopathy |
08) Imaging
- USG Abdomen: Bulky pancreas with peripancreatic fluid collection
- CT Abdomen (CECT): Balthazar Grade E pancreatitis
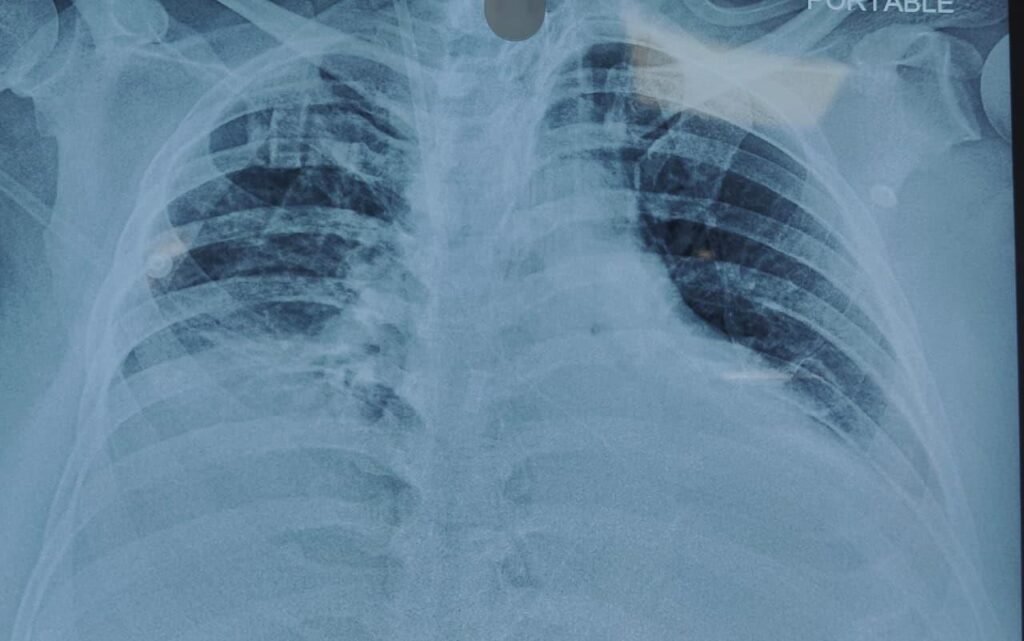
- Chest X-ray: Bilateral diffuse infiltrates — ARDS pattern
09) ECG & RBS
- ECG: Sinus tachycardia, no ST-T changes
- RBS: 220 mg/dL (stress hyperglycemia)
10) Emergency Stabilization (Day 0 – ER)
- Airway: Intubated and placed on Volume Control Ventilation (VT 6 mL/kg, FiO₂ 0.6, PEEP 10)
- Breathing: ARDS protocol initiated
- Circulation:
- Noradrenaline 0.1 µg/kg/min → titrated to maintain MAP ≥ 65 mm Hg
- IV Ringer’s Lactate 20 mL/kg in first 2 h (goal-directed fluid resuscitation)
- Central & Arterial line inserted
- Drugs:
- Inj. Meropenem 1 g IV TDS
- Inj. Pantoprazole 40 mg IV OD
- Inj. Paracetamol 1 g IV TDS
- Inj. Fentanyl infusion 1 µg/kg/h
- Insulin infusion 1 U/h (target 140–180 mg/dL)
- IV Calcium gluconate 10 mL slow IV if Ca²⁺ < 7 mg/dL
11) Day-by-Day ICU Care
- Day 1: Resuscitation Phase
- On VCV with PEEP 10, FiO₂ 0.6
- Noradrenaline + Vasopressin support
- Fentanyl sedation + Midazolam 1 mg/h
- Meropenem 1 g IV TDS + Metronidazole 500 mg IV TDS
- Fluid target: 3 L/24 h balanced crystalloids
- Urine output: 0.2 mL/kg/h → started furosemide 20 mg IV BD
- Electrolyte correction: Mg²⁺ and Ca²⁺ replaced
- RRT planned if Cr > 3.5 or anuria > 12 h
- Day 2: Organ Support Escalation
- Persistent oliguric AKI → started CRRT (CVVH mode)
- FiO₂ decreased to 0.5, PEEP 10
- Vasopressors tapered slowly
- Meropenem continued, cultures sent (blood, urine, ET aspirate)
- Started Enteral Nutrition via NJ tube (trickle feeds 20 mL/hr)
- Monitored RFT, ABG, lactate, I/O hourly
- Day 3: Clinical Turning Point
- Urine output improving (0.8 mL/kg/h)
- CRRT paused
- FiO₂ down to 0.4, PEEP 8 → PaO₂/FiO₂ = 180
- Noradrenaline reduced to 0.02 µg/kg/min
- Pain managed with Paracetamol 1 g IV TDS
- Insulin infusion → SC insulin sliding scale
- Physiotherapy: Passive limb movement + chest physiotherapy BD
- Day 4: Stability Achieved
- Off vasopressors, hemodynamically stable
- PEEP 8 → 6, FiO₂ 0.35
- Meropenem 1 g IV TDS (day 4 of 7)
- DVT prophylaxis: Enoxaparin 40 mg SC OD
- Stress ulcer prophylaxis: Pantoprazole 40 mg IV OD
- Cremaffin 20 mL HS for bowel movement
- Nutrition: Peptamen 50 mL/hr continuous feed
- Day 5: Recovery & Diuresis
- On PSV mode ventilation, alert and following commands
- Analgesia: Paracetamol 1 g IV TDS
- Meropenem continued (day 5/7)
- Furosemide 20 mg IV OD – achieved negative balance
- Electrolytes normalized
- DVT prophylaxis & limb physiotherapy continued
- Day 6: Extubation Day
- Successfully extubated to HFNC → nasal cannula 2 L/min
- Antibiotic course (Meropenem) completed
- Switched to oral Pantoprazole 40 mg OD
- Oral feeding initiated (soft diet + supplement BD)
- Mobilization with physiotherapy BD
- Day 7: Ward Transfer
- Stable vitals on room air
- Creatinine 1.1 mg/dL, urine output 2 mL/kg/h
- Off sedation, fully conscious
- Pantoprazole 40 mg PO OD, Paracetamol 1 g PO TDS PRN, Thiamine 100 mg BD
12) Pathophysiology
- Initiation
- Trigger (e.g., alcohol, gallstones) → Premature activation of trypsinogen inside acinar cells.
- Leads to autodigestion of pancreatic tissue.
- Inflammation Cascade
- Activated trypsin, elastase, and phospholipase A₂ damage acini, ducts, and surrounding fat.
- Release of cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6) causes Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS).
- Vascular Leak & Shock
- Massive capillary leak → third spacing of fluids → hypovolemia.
- Cytokines cause vasodilation → distributive + hypovolemic shock.
- Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
- Renal hypoperfusion from shock and cytokine storm.
- Acute tubular necrosis develops → ↑ Creatinine, oliguria.
- Septic Shock
- Necrotic pancreatic tissue gets infected (gram-negative bacteria).
- Endotoxin release → refractory hypotension despite fluids → needs vasopressors.
- ARDS
- Cytokines and enzymes enter pulmonary circulation → alveolar-capillary damage, → ↑ permeability, non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema, ↓ compliance → ARDS.
- Multiorgan Dysfunction
- Worsening hypoxia, renal shutdown, metabolic acidosis, encephalopathy, and coagulopathy follow if untreated.
13) Discharge Medicines
| Drug | Dose | Mechanism | Purpose |
| Pantoprazole | 40 mg OD | PPI | Stress ulcer prevention |
| Paracetamol | 500 mg TDS PRN | COX inhibition | Analgesic |
| Thiamine | 100 mg BD | B1 coenzyme | Prevent Wernicke, energy metabolism |
| Multivitamin | 1 OD | Nutritional | |
| Peptamen supplement | 1 scoop BD | Protein support | Nutrition |
| Cremaffin | 20 mL HS | Osmotic laxative | Bowel regularity |
14) Key Notes / Clinical Pearls
- Early aggressive fluid resuscitation (first 24 h) saves organs.
- Avoid over-resuscitation — may worsen ARDS.
- Enteral > Parenteral feeding once gut functional.
- Monitor Ca²⁺ and TG levels daily in severe cases.
- Sterile vs infected pancreatitis differentiation is crucial (guided by PCT/culture).

